In a world moving towards a cashless society, the question arises: Can a business refuse cash payments?
This article aims to provide a detailed overview of the legality of refusing cash, the reasons behind such a policy, the challenges it presents, and alternative payment options.
By understanding these aspects, businesses can make informed decisions while considering cashless strategies.
Can a Business Refuse Cash? Is it legal?
Refusing cash payments is generally legal in the United States, but there are important factors to consider.
Federal law stipulates that U.S. currency is acceptable for all debts public and private, but does not require businesses to accept cash payments for every transaction.
For example, businesses are allowed to refuse cash payments if it exceeds a certain amount, typically $10,000, to comply with the Currency and Foreign Transactions Reporting Act. Additionally, federal law permits refusal of currency deemed to be suspicious or counterfeit.
State laws can add to federal regulation, and it is important to understand the specific laws in each state where a business operates. Several states have made it illegal to refuse cash payments for certain transactions, such as for taxation payments and utility bills.
In addition, there may be legal issues surrounding discrimination, as a cashless policy could be exclusionary for individuals without access to digital payment methods.
The ongoing pandemic has brought additional concerns, with some businesses preferring cashless transactions to minimize contact and reduce the risk of virus transmission.
Nevertheless, businesses must have a solid understanding of the potential legal, economic, and social implications of going completely cashless.
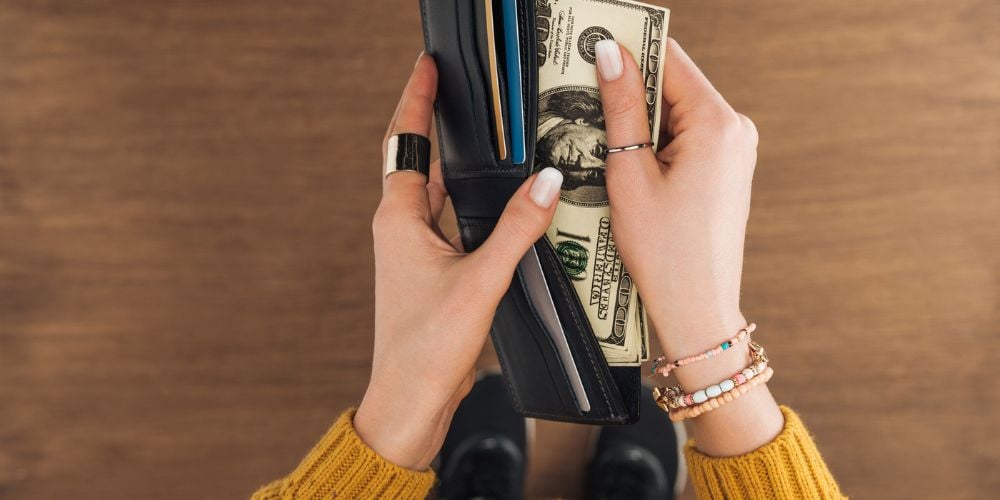

Reasons for refusing cash payments
Businesses may choose to implement a cashless policy for various reasons. Increased efficiency is one of the most significant benefits, as cashless transactions require less physical handling and processing, saving time and resources.
Automation of payment processing also reduces the likelihood of errors and the need for manual reconciliation.
Cashless payments also reduce the risk of theft and fraudulent activities. Cash transactions involve physical cash handling, increasing the likelihood of thefts, while electronic transactions are more secure and less vulnerable to theft and counterfeiting.
Moreover, cashless payments align with current customer preferences and behaviors. Consumers prefer more convenient and safer payment methods for transactions.
Additionally, millennials, who are a significant part of the customer base, expect digital payments options to be available for the majority of transactions.
Challenges of cashless payments
While embracing a cashless payment system seems good for business and customer convenience, several challenges come along with it. One potential downside is the issue of access and equity.
Not everyone has access to or prefers digital payment methods, leading to exclusion which could be problematic for small businesses and low-income individuals.
Discrimination and human rights concerns also arise. Going cashless could lead to further exclusion of low-income and marginalized communities while privileging higher-income and tech-savvy individuals.
Furthermore, digital transactions could pose privacy and security risks, with sensitive consumer information potentially vulnerable to hacking.
In addition to social and ethical issues, the cost of implementing, maintaining, and updating a cashless payment system could be a challenge for businesses.
Small businesses, in particular, may face difficulty affording the necessary software and hardware to offer cashless payment options.
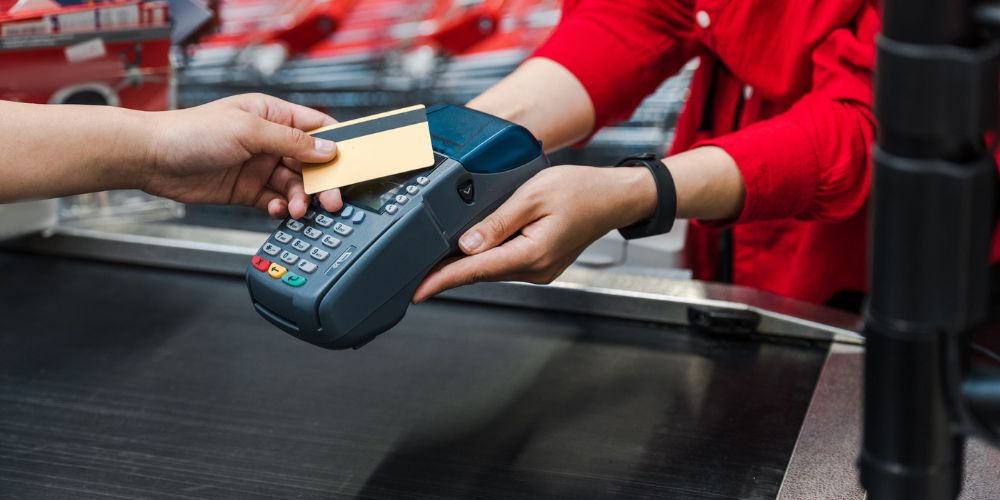
Alternatives to cash payments
In balancing the benefits and shortcomings of a cashless payment system, businesses can offer alternative payment options that cater to different customers’ needs.
Credit cards and debit cards have become the preferred payment method for most consumers and offer greater convenience and security.
Mobile payment apps such as Google Pay, Apple Pay, Samsung Pay, and Venmo provide electronic alternatives to cash transactions and allow for encrypted and secure payment processes.
Gift cards, coupons, and vouchers are popular alternative payment options that can help businesses reduce the need for physical cash handling while still providing customers with flexible payment options.
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, though still largely untested, also offer alternative payment methods for businesses looking into the future.

Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the advantages of refusing cash and adopting cashless payments?
Ans: Cashless payments offer increased efficiency, improved security, and reduced risk of theft for businesses, while also aligning with customer preferences.
What challenges does a cashless society present?
Ans: Challenges include discrimination concerns, unequal access to financial services, and potential privacy and security issues.
How can businesses ensure inclusivity while adopting cashless strategies?
Ans: Businesses should balance the benefits of cashless payments with the need to cater to diverse customer bases, offering alternative payment options and considering potential socioeconomic implications.
Conclusion
Businesses generally have the legal right to refuse cash payments, but certain exceptions apply. Cashless transactions offer various benefits, from heightened efficiency to meeting customer preferences.
However, challenges such as discrimination, access and equity, and privacy concerns must also be considered. By offering alternative payment options, businesses can cater to a diverse customer base while embracing the benefits of a cashless society.
Remember, embracing cashless strategies should be a thoughtful decision considering the legalities and socioeconomic factors at play.
As technology continues to advance and consumer behaviors evolve, businesses must adapt to the changing landscape while ensuring inclusivity and the protection of consumer rights.


 Tags:
Tags: