Equilibrium in economics is essential as it denotes the point where the supply of goods matches demand.
But, wanna know why is equilibrium important in economics?
Well, this concept is pivotal in both microeconomics, concerning individual players in the market, and macroeconomics, which covers the economy as a whole.
Understanding equilibrium helps to grasp how markets function and predict future changes in prices and quantities.
The Concept of Equilibrium
Definition and Basics
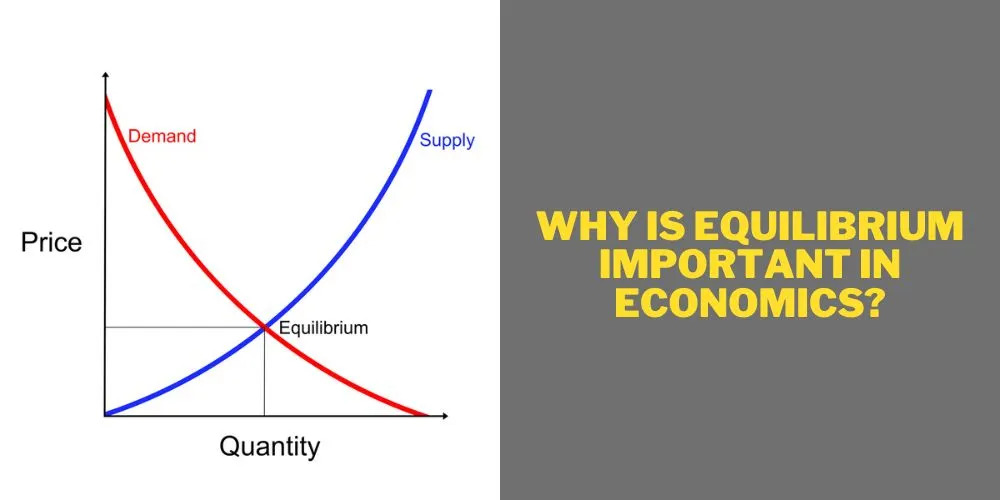
Economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces are balanced. In this state, there is no external influence causing changes. This occurs in a perfect scenario where the amount of goods buyers want equals the number sold.

Types of Equilibrium
Market equilibrium pertains to a specific market. General equilibrium covers various markets in an economy.
Partial Equilibrium looks into only a single part while keeping other areas constant.
Theoretical Framework
The Law of Supply and Demand is central here. Equilibrium is reached when the price allows the quantity demanded by consumers to equal the quantity supplied by producers. The price mechanism helps achieve this balance.
Why Is Equilibrium Important In Economics?
Allocative Efficiency
When markets reach equilibrium, resources are allocated efficiently. Producers supply the right amount of goods at the right price, meeting consumer demand without causing waste or shortages.
For instance, in competitive markets like coffee, equilibrium ensures that the amount of coffee produced meets consumers’ needs at prevailing prices.
Market Stability
Equilibrium brings stability to markets, avoiding price volatility and ensuring continuity of supply. For example, in the stock market, equilibrium can prevent sudden stock price jumps, which can lead to market crashes or bubbles.
Predictability and Planning
Equilibrium models offer ways to forecast future market conditions, facilitating better planning and decision-making for businesses and governments.
For instance, if equilibrium prices for raw materials are known, a factory can budget more efficiently for production costs.
Consumer and Producer Surplus
At equilibrium, both consumer and producer surplus are maximized. Consumers pay a price that reflects the maximum willingness to pay minus the market price, benefiting from the difference.
Producers sell their goods at the market price, which is usually above their minimum acceptable price.
Equilibrium and Economic Health
A healthy economy often reflects a state of equilibrium. When equilibrium exists, it usually coincides with low unemployment rates and stable inflation.
These indicators help economists gauge overall economic well-being.
Factors Disturbing Equilibrium
External Shocks
Events like natural disasters or political changes can disrupt supply and demand. For instance, a hurricane damaging a major factory can reduce supply, shifting the equilibrium price.

Government Policies
Taxes and subsidies can shift supply and demand. A new tax on tobacco raises costs for producers, who may pass these costs on to consumers, altering market equilibrium.
Technological Changes
Advances in technology can disrupt traditional equilibriums by introducing new products or more efficient production methods.
The rise of electric vehicles, for instance, is shifting demand away from gasoline cars to battery-powered ones.
Adjusting to a New Equilibrium
Markets adjust to a new equilibrium through mechanisms such as price changes, which restore the balance between supply and demand.
Entrepreneurs play a key role by identifying new opportunities and shifting resources to meet changes in consumer preferences.
Pro Tips for Understanding and Analyzing Equilibrium
To understand market movements, graphical analysis is invaluable. Keeping up with economic indicators also helps identify shifts in equilibrium.
By studying both historical and modern case studies, one can see economic theories in action, providing a deeper understanding of market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between micro and macroeconomics in terms of equilibrium?
Microeconomics looks at individual markets while macroeconomics views the economy as a whole. Both areas use the concept of equilibrium to analyze market dynamics, though the scales differ.
Does equilibrium require government intervention?
Markets can reach equilibrium without intervention if left to their own devices. However, government actions can help correct market failures and ensure more socially optimal outcomes.
How does technological innovation affect market equilibrium?
Initially, technology can disrupt market equilibrium by introducing superior products or more efficient methods. However, over time, markets adjust to this innovation and establish a new equilibrium.
What are common misconceptions about economic equilibrium?
Many assume that equilibrium means the economy or market is in a perfect state. However, it merely indicates that supply equals demand. Equilibrium does not account for externalities or indicate that all social or economic issues are resolved.
How can understanding equilibrium help in making better business decisions?
Knowing where the market is headed helps businesses anticipate changes in costs, prices, and consumer behavior, allowing for better strategic planning and resource allocation.
Conclusion
Understanding equilibrium is fundamental to grasping how economies operate. It informs everything from policy decisions to business strategy.
As our economies continue to evolve, especially with advancements in technology and globalization, the importance of equilibrium will likely grow.

 Tags:
Tags:










