A stock option can be a beneficial tool when building your investment portfolio. But before considering whether or not to buy, you may ask yourself, “What is an option in stocks, and how can it benefit me?” As you continue reading, you may just find the answer you’re looking for.
How A Stock Option Works
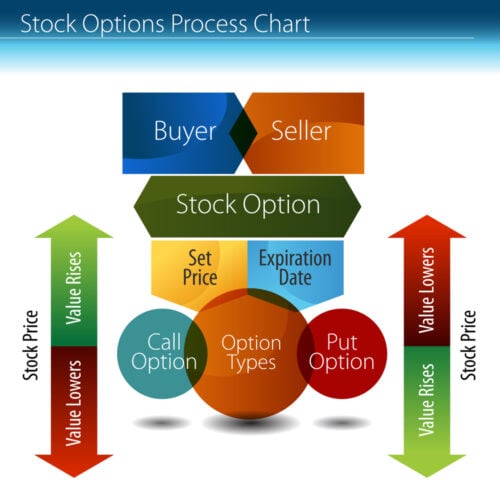
A stock option is a contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell shares of a particular stock at a specified price within a certain period of time. The value determines the difference between the underlying stock price and the strike price.
Stock options are often used as a form of incentive compensation, allowing employees to share the company’s success without incurring any upfront cost. Options are also popular with investors as a way to hedge against losses in the underlying stock.

Option Styles
There are two types of stock option styles: American-style and European-style. The American-style option can be exercised any time up until the expiration date, while the European-style option can only be exercised on the expiration date itself.
The price at which the option can be exercised is known as the strike price. Options are typically quoted with the strike price first, followed by the premium.
Option Types
There are two types of options: put options and call options.
A put option gives the holder the right to sell an asset at a certain price, while a call option gives the holder the right to buy an asset at a certain price.
Both put and call options are traded on exchanges, and both have expiration dates. The key difference between a put option and a call option is the direction in which the holder expects the asset’s price to move.
Stock Option Price Components
The price of an option is made up of two components: the intrinsic value and the time value.
Intrinsic Value
The intrinsic value is the difference between the strike price and the current market price of the underlying stock. If the current market price of the stock is greater than the strike price, then the option is said to be in the money and has intrinsic value.
If the current market price of the stock is less than the strike price, then the option is said to be out of the money and does not have intrinsic value.

Time Value
The time value is the amount by which the option premium exceeds the intrinsic value. It represents the chance that the stock price will move in favor of the option holder before the option expires.
The time value is also affected by factors such as the time to expiration, the market volatility of the underlying stock, and the interest rate.
As an option gets closer to expiration, its time value declines. This is because there is less time for the stock price to move in favor of the option holder.
Some explanations of keywords that are important to understand when understanding time value and stock options can be found below.
Market volatility: It is a measure of how much the price of a stock fluctuates. A higher volatility means that the stock price is more likely to move in favor of the option holder.
Interest rate: It is used to calculate the time value of an interest-rate-sensitive option, such as a call or put option. A higher interest rate decreases the time value of an option.
Premium: It is the price of the option contract. It is made up of the intrinsic value and the time value.
Example of Stock Options
For example, an option quote for XYZ stock might look like this:
XYZ 100.00 (25.00)
This means that the option has a strike price of $100 and a premium of $25. The option is therefore priced at $125 ($100 strike price + $25 premium).
The holder of a call option has the right to buy shares of the underlying stock at the strike price, while the holder of a put option has the right to sell shares of the underlying stock at the strike price.
Options can be bought and sold on exchanges or over-the-counter (OTC). OTC options are typically less expensive than exchange-traded options, but they are also more illiquid.
Options contracts are typically for 100 shares of the underlying stock, but they can also be for other amounts, such as 10,000 or even 1 million.

Should You Buy a Stock Option?
There are many factors to consider when making the decision to buy a stock option. The most important factor is timing. When considering whether or not to buy a stock option, you must first assess the current market conditions.
If the market is in a downturn, it may not be the best time to buy an option. However, if the market is currently experiencing growth, buying an option could be a good way to profit from the market trend.
Another important factor to consider is the strike price of the option, the price at which you can buy or sell the underlying stock.
You should compare the strike price to the current market price of the stock. If the strike price is lower than the current market price, buying the option could be a good way to make a profit.
It’s also beneficial to consider the expiration date of the option when making your decision. The expiration date is the date at which the option expires and can no longer be traded.
Options that are close to expiration are less likely to make large profits than those that are further from expiration.

Final Thoughts: What is an Option in Stocks?
Although stock options can be a valuable investment tool, they come with risks. It is important for investors to understand the risks and rewards associated with stock options before making any decisions.
By understanding how stock options work and taking into account individual circumstances, investors can make informed choices about whether or not to use stock options in their portfolios.


 Tags:
Tags:










